What I read this week...
Honey, I shrunk Starlink, Lockheed Martin powers NOAA's next-gen spacecraft for weather forecasting, and Sierra Space's Dream Chaser sets for launch.
This week's newsletter is brought to you by saphira.ai: solutions to simplify safety and reliability compliance.
TLDR
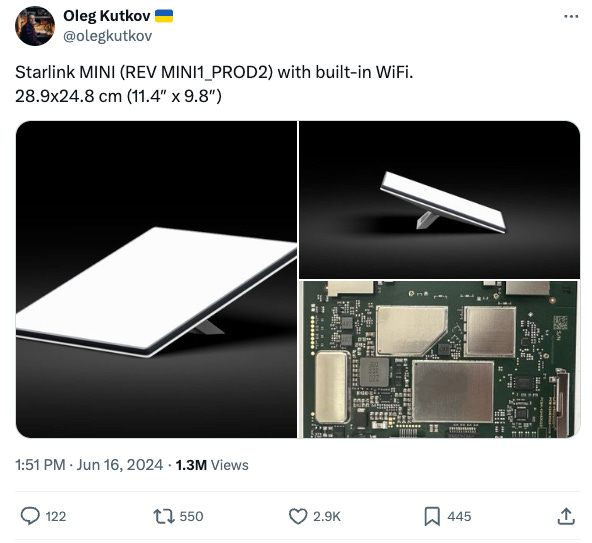
SpaceX has unveiled a new, more affordable Starlink Mini dish, designed to fit in a backpack and integrated with a Wi-Fi router. This compact device, measuring 11.4 by 9.8 inches, is expected to cost between $250 and $300, approximately half the price of the standard dish. Performance tests reveal download speeds of 100 Mbps and upload speeds of 11.5 Mbps with a 23ms latency, making it suitable for 4K streaming and casual gaming. The rollout will commence in select areas in the coming months.
NASA has chosen Lockheed Martin to build NOAA's next-generation spacecraft. These advanced spacecraft will enhance weather forecasting and environmental monitoring, providing critical data for disaster response and climate research. Lockheed Martin's selection follows their history of successful collaborations with NASA, promising significant improvements in the accuracy and timeliness of weather data.
Sierra Space's Dream Chaser spaceplane is set for its inaugural mission. The spaceplane aims to revolutionize space travel by providing a reusable, versatile vehicle for transporting cargo and eventually crew to and from low Earth orbit. This development is a crucial step towards more sustainable and cost-effective access to space, with implications for both commercial and governmental space missions.
Technical Deep Dive
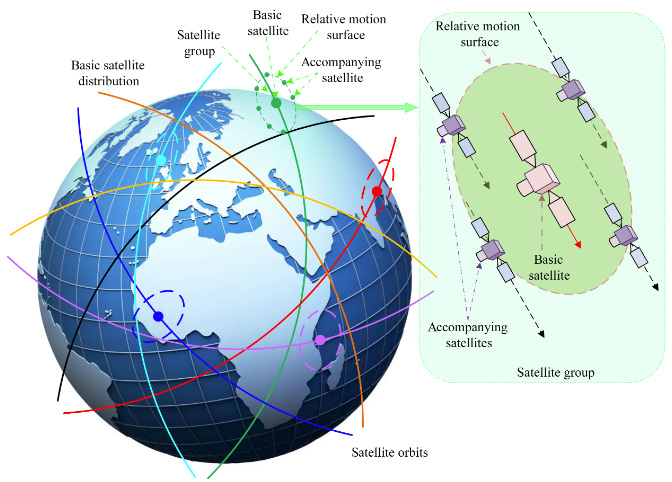
A recent research paper titled "Configuration Design Method of Mega Constellation for Low Earth Orbit Observation" presents a novel method for designing satellite constellations optimized for Earth observation. This method addresses the challenges of nonlinear problems in complex space environments by proposing a configuration that includes:
Satellite imaging width considerations.
Formation flying of subgroup satellites.
Global uniform coverage by payloads.
The research introduces a configuration where basic satellites are surrounded by accompanying satellites. This setup enhances intersatellite interaction, improves observation quality, and ensures rapid response to observation missions. Using Nondominated Sort Particle Swarm Optimization (NS-PSO) algorithm under a High Precision Orbit Propagator (HPOP) model, the method achieves precise orbit determination, ensuring the constellation's stability and efficiency over time. The full research can be accessed here.
Deal Flow
Basalt is emerging as a significant player in the space industry, innovating in satellite technology (Basalt).
Autify has secured $13 million in Series B funding and launched Zenes, an autonomous AI agent for software quality assurance (PR Newswire).
Apex raised $95 million to boost satellite bus production, enhancing their capacity to meet growing demands in the space sector (SpaceNews).
Spanish startup secures funds to deploy a commercial IoT constellation, expanding its capabilities in the global IoT market (SpaceNews).
Raspberry Pi is now a public company, with its shares surging post-IPO pricing, indicating strong market interest and confidence (TechCrunch).
Ardian and Saudi’s PIF acquire a 37.6% stake in Heathrow, with Ferrovial retaining a 5% share, indicating significant investment and interest in critical infrastructure (Reuters).
About Saphira.ai
Saphira is a Y Combinator-backed software tool to define and monitor hardware throughout development. Engineers use it to organize design information that otherwise gets buried in piles of documents, pre-emptively understand when subsystem changes break end-to-end safety scenarios and ultimately deliver safer, higher-quality hardware more quickly. Learn more here.