What I read this week...
SpaceX's Polaris Dawn mission launches July 31. Australia and the US formalize a Technology Safeguards Agreement. Japan launches ALOS-4 satellite with H3 rocket.
This week's newsletter is brought to you by saphira.ai: solutions to simplify safety and reliability compliance.
TLDR
SpaceX is gearing up for the Polaris Dawn mission, scheduled for launch on July 31. This mission aims to conduct scientific research and technology demonstrations in low Earth orbit. What makes Polaris Dawn unique? The crew, led by billionaire Jared Isaacman, includes a mix of experienced astronauts and private individuals. The mission will feature several firsts, including the highest Earth orbit ever reached by a crewed spacecraft since the Apollo missions. Additionally, the crew will conduct the first-ever commercial spacewalk. This mission highlights the increasing role of private companies in space exploration, pushing the boundaries of human spaceflight capabilities.
Australia and the United States have formalized a Technology Safeguards Agreement (TSA) to enhance cooperation on space-related technologies, including rockets and satellites. How does this agreement impact the space industry? The TSA establishes a legal framework to ensure that sensitive technology used in joint space projects is protected. This is particularly important for the growing collaboration between the two countries in space exploration and satellite launches. By safeguarding technological information, the agreement facilitates smoother collaboration, allowing both nations to leverage each other’s expertise and resources, thereby accelerating advancements in space technology.
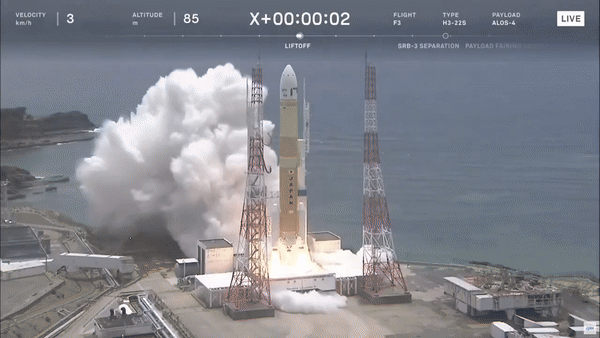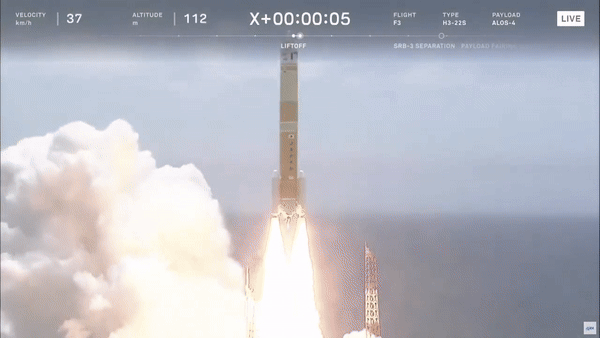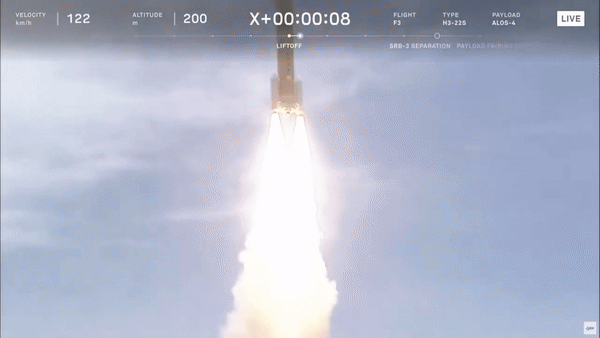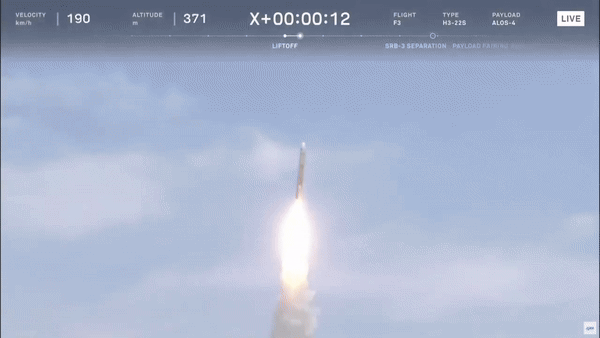
Japan launched its ALOS-4 Earth observation satellite aboard the H3 rocket. What is the significance of this launch? The ALOS-4 satellite is designed for advanced Earth monitoring, providing high-resolution imagery for disaster management, environmental monitoring, and resource management. The H3 rocket, developed by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and JAXA, represents Japan’s latest innovation in launch vehicle technology, aiming to provide more cost-effective and reliable access to space. This mission underscores Japan’s commitment to enhancing its space capabilities and contributing valuable data for global environmental and disaster response efforts.
Technical Deep Dive
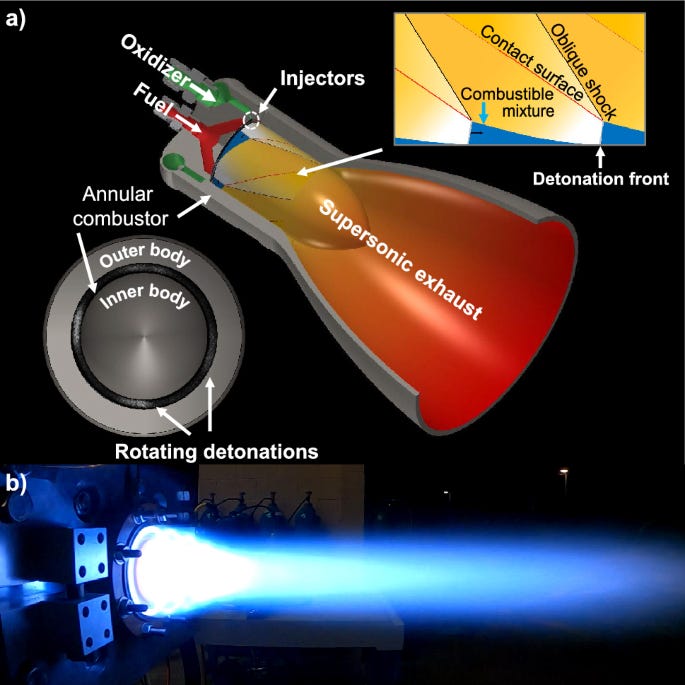
"Experimental Validation of Rotating Detonation for Rocket Propulsion" explores advanced methods to enhance rocket propulsion efficiency using Rotating Detonation Rocket Engines (RDREs). This approach addresses challenges in traditional rocket engines by leveraging supersonic combustion-driven shock waves.
Optimal Performance Metrics:
Detonation Benefits: RDREs provide up to 10% increased thrust, reduced engine size and weight, lower injection pressures, and less susceptibility to acoustic instabilities.
Stable Detonation Waves: Consistent operation across various flow conditions, emphasizing the importance of controlled inlet boundary conditions.
Key Findings:
Performance Consistency: Achieving reliable RDRE operation across all facilities, validating the robustness of detonation-based propulsion.
Reduced Uncertainties: Detailed analyses ensured reliable and repeatable performance metrics.
Implications and Future Directions:
Enhanced Rocket Propulsion: RDREs offer higher thrust, improved efficiency, and reduced engine weight and size.
Further Development: Ongoing research will refine RDRE designs and integrate this technology into practical aerospace applications, potentially revolutionizing space travel.
The study demonstrates RDREs' potential to significantly improve rocket propulsion efficiency, paving the way for future advancements in aerospace technology.
Deal Flow
Latitude has secured €15M in the France 2030 call for projects to advance its rocket development and enhance Europe's independent access to space (Payload Space).
Sift has raised $17.5M in a Series A funding round to expand its space telemetry technology and market reach (Payload Space).
Italy is significantly increasing its investments in the US space sector to strengthen bilateral cooperation and technological exchange (Payload Space).
NATO is enhancing its space capabilities through various initiatives, emphasizing the strategic importance of space in defense and security (NATO).
About Saphira.ai
Saphira is a Y Combinator-backed software tool to define and monitor hardware throughout development. Engineers use it to organize design information that otherwise gets buried in piles of documents, pre-emptively understand when subsystem changes break end-to-end safety scenarios and ultimately deliver safer, higher-quality hardware more quickly. Learn more here.